This site is intended only for the use of Nordics Healthcare Professionals
Highlights

Crohns Disease Exclusion Diet - CDED: New insights and updates
The acknowleded pediatric gastroenterologist and researcher Johan Van Limbergen will during this webinar guide you throught the rationale behind nutritonal therapies for IBD and give updates on the latest CDED research.
See moreArticle
Introduction/overview Chronic pancreatitis is a progressive and irreversible inflammatory disease of the pancreas. This results in exocrine and endocrine dysfunction which in time leads to maldigestion and malabsorption reducing the body’s ability to utilise essential macro and micronutrients. Consequently protein energy malnutrition is common. Research indicates that in more than 80...
"ENTERAL TUBE FORMULA: A MULTICENTRE TRIAL IN THE UNITED KINGDOM The prevalence of Cerebral Palsy (CP) children who require a low-calorie feed is between 8-15%. ESPGHAN working group recommend using a low-fat, low-calorie, high fibre, micronutrient replete formula for immobile Neurological Impaired children. Children aged 1-11 years with neurological issues were recruited from UK National Health Service (NHS). Participants were given the new low-c..."
The prevalence of children with complex neuro-disability has increased due to advances in the medical management of preterm infants and improved care for children with severe neurological impairment . Neuro-disability covers a wide range of clinical conditions, including acquired brain injury, epilepsy and learning disability. Neuro-disabilities present a significant disease burden for the child and family, with the focus for families to promote the best possible participation in life for all affected.Children with neuro-disabilities can be significantly disadvantaged in their ability to nourish themselves due to poor hand to mouth motor coordination, along with disordered swallowing, resulting in aspiration of food in the lungs. The length of feeding time may be considerably increased and instead of mealtimes being an enjoyable experience, they are distressing for both child and carer. These impairments in feeding eventually lead to undernutrition and invariably children require a feeding tube to ensure nutritional requirements are met. Although tube feeding improves overall nutritional status, it has also been associated with an excess deposition of body fat compared with typically developing children. Children with neuro-disability are at risk of becoming overweight because of their low activity and psychosocial constraints. Additionally, children with a neuro-disability tend to grow slowly for non-nutritional reasons and have altered body composition due to underdeveloped skeletal muscle. Children are more likely to be overweight and tend to have low lean muscle mass - therefore a low BMI in this group does not necessarily imply low fat stores. Efforts are needed to protect severely disabled children from overfeeding and to help families of children with neuro-disabilities to manage their child’s weight.Children with neuro-disabilities who are fed to 80% of their estimated average energy requirements have reported a positive energy balance resulting in high body fat mass. Of note, any attempt to dilute the existing proprietary feeds to reduce the calorie intake to a level commensurate with the energy expenditure of a child with a disability is likely to have an adverse impact on micronutrient and protein intake.The clinical nutrition industry has responded to this need and developed commercially available enteral formulas that are low in energy but nutritionally adequate for protein and micronutrients, essential for developing children who are reliant on enteral formula to supply a major proportion of their intake [8]. Additionally, feed tolerance is generally worse in children with neuro-disabilities, associated with comorbidities including epilepsy, posture and tone disorders, and medications used for the treatment of these conditions can further exacerbate gastrointestinal function. Common feed related symptoms associated with neuro-disabilities include vomiting, retching, pain associated with feeding - feedinduced dystonia, constipation, and gastrointestinal dysmotility.The aim of this national multicentre retrospective study was to monitor the effectiveness of a low energy hydrolysed enteral formula on weight management, feed tolerance and health economics in children with a neuro-disability.
Melkeskolen – del 1 (Vibeke Fossum): Som helsesykepleier møter man ofte små barn med diffuse symptomer som kan minne om melkeallergi. Men når skal man mistenke melkeallergi? Hvordan skille mellom sutrete normale barn og syke barn? Hvordan stilles diagnosen kumelkproteinallergi, og hva er veien videre for mor og barn? Barnelege Vibeke Fossum vil gi deg svare på dette og mye mer.
This case study discusses the nutritional management of a severely undernourished patient with head and neck cancer. The patient experienced diarrhoea and significant weight loss, despite the use of various enteral formulas and delivery methods (continuous and bolus feeding). Thereafter a combination of products within the Peptamen® range were trialled. A marked reduction i...
Can Human Milk Oligosaccharides modulate the allergic response and improve the management of cow's milk protein allergy?
Eat10 – A quick and easy screening tool, validated to identify those at risk of Dysphagia.
Differentiating milk allergy (IgE and non-IgE from lactose intolerance: understanding the underlying mechanisms and presentations.
To characterize the peptide profile of a whey-based, extensively hydrolysed formula (eHF) prepared with a non porcine enzyme blend, and to assess whether it meets the hypoallergenicity criteria of the Ame...
The aim of the symposium was to share learnings from the recently established European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology (EAACI) Task Force on special products for cow’s milk protein allergy (CMPA), with the intention of providing an overview on controversies regarding extensively hydrolysed formulas (eHFs), their utility, and the validity of the definition ‘special products ...
To determine whether an extensively hydrolyzed formula (EHF) supplemented with two human milk oligosaccharides (HMO) was tolerated by infants with cow’s milk protein allergy (CMPA). Methods: A whey-based EHF (Test formula) containing 2′fucosyl-lactose (2′FL) and lacto-N-neotetraose (LNnT) was assessed for clinical hypoallergenicity and safety. The Control formula was...
Recently, as reported by dietetic departments in the United Kingdom, we have seen an increase in Homemade Blended Diets (HBD) being given to children requiring tube feeding. HBD practice may increase the risk of tube occlusion and nutritional inadequacies. In 2015 the British Dietetic Association (BDA) developed their first ‘Practice toolkit liquidised food via gastrostomy tube’, whic...
Many patients requiring long term enteral nutrition have neurological disorders, such as motor neurone disease (MND) or Huntington’s disease (HD). In our experience, a proportion of these individuals may struggle to tolerate enteral feeding despite optimising medical management and excluding obvious gastrointestinal pathology. In MND, prolonged reduced mobility, weaknes...
Major trauma refers to significant or multiple injuries that could result in death or severe disability, sustained from a traumatic insult such as a road traffic collision, fall, sporting accident, or physical assault. It is the leading cause of death and major disability in people aged under 45 years in the UK.1 Critically injured patients are often managed on ...
Videos
This lecture will cover key topics, including the typical symptoms and predictors of GERD in children, as well as overlapping symptoms that may indicate other diagnoses. Dr. Ralf Heine will discuss the diagnostic criteria and current international and nordic guidelines for assessment, along with recommended treatment options. Additionally, the session will explore the connections between Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (FGID) and Cow's Milk Protein Allergy (CMPA), highlighting relevant research that informs clinical practice.
During the webinar, we will place great emphasis on the importance of protein and protein quality in nutritional treatment. We are happy to have Dr. Martin Hagve, PhD, Chief physician and Specialist in Gastroenterological Surgery, University Hospital of North-Norway, Associate Professor at UiT - The Arctic University of Norway, as lecturer. During the presentation, Dr. Martin will go through existing guidelines and share his experience from everyday clinical practice and how to best reach the patients’ protein targets. The webinar is held in English.
In this 45 min webinar you can listen to pediatrician and phd Carina Saunders discuss recent research on early development of the microbiome, from pre-birth to solid foods. Even before birth the gut microbiome starts developing. After that there’s several environmental factors that become important in this development. Dr.Saunders also touches on subjects such as early introduction of allergens and composition of diet ones the child starts solid foods.
Föreläsning av Maria Rehbinder, leg. dietist Maria har en gedigen erfarenhet av att arbeta med kostbehandling till patienter som har diabetes. Under föreläsningen delar Maria med sig av vad som är viktigt att tänka på när man har en patient som har undernäring och samtidig diabetes framför sig, och vad det är som man ofta missar att tänka på. Maria ger dessutom ge konkreta råd och förslag kring kostbehandlingen, och delar med sig av hur hon tänker kring energi- och proteinbehov, kolhydratintag, fördelning av makronutrienter, berikning av mat, och vad som är viktigt att ta hänsyn till vid val av näringsdryck.
Diagnosis of functional disorders in infants poses a challenge to clinicians as symptoms of different conditions often overlap or simply represent normal infant behaviors. CoMiSS™ can support clinicians in determining if symptoms are related to cow’s milk or not.
In the webinar, the important role of protein and protein quality in the nutritional treatment will be highlighted. Professor Philipp Schuetz will talk about the importance of malnutrition management and individualized nutritional support to improve patients’ outcome. Additionally, Ola Wallengren will give insights on what role protein and protein quality have in the nutritional treatment, along with current protein recommendations and strategies to meet them.
Anna Asarnoj, MD PhD, Associate Professor, Consultant Pediatrician and Pediatric Allergist, gives this two part lecture on both prevention, diagnosis and treatment of allergies. Log in to see the full lecture.
With age, we gradually begin to lose muscle mass, bone mass and strength. Sarcopenia is a serious condition which becomes more common with age and is characterized by a progressive loss of skeletal muscle mass and strength, which results in functional decline and is associated with an increased risk of adverse health outcomes.
This real-world evidence study explores the results from a UK multi-centre retrospective study of children who have switched to a tube feed containing food-derived ingredients. Read the publication, or watch our webinar where speakers discuss the positive outcomes and the potential impact they might have on local guidelines or day to day clinical practice.
Video demonstrating the normal swallowing process.
Learn more about MCTs and their role in reducing fat malabsorption
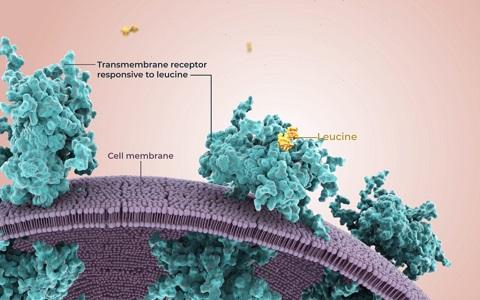
High-quality milk protein contains high levels of essential branched chain amino acids. The branched chain amino acid leucine is particularly a potent stimulator of muscle protein synthesis. This video shows you the mechanism of how leucine stimulates the muscle protein synthesis.
We have seen increasing interest in using blenderized real food for enteral nutrition. How is the trend evolving, what is the impact on pediatric patients, and should it be supported by healthcare professionals?
Cerebral palsy (CP) is among the most common neurological impairment. It is caused by nonprogressive damage or malformation while the brain is developing and can affect individual’s speech, motor skills, vision, memory, muscle actions, and learning abilities. The symposium chaired by Prof. Frederic Gottrand highlight the advances in supportive care that have extended the life expectancy of people with CP while also pointed to a key problem experienced by patients: chronic undernutrition or malnutrition. Prof. Gottrand presented strategies in nutritional management of CP including the importance of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy to help patient reaching his nutritional needs. Prof. Claudio Romano, put emphasis on the use of fiber in enteral nutrition for CP patients and its benefit in improving nutritional status, diarrhea and constipation. Click here for more information.
This webinar dives into the emerging trend of blended diets for enteral feeding. There is some evidence to suggest that blended diets, used solely or in combination with commercially available enteral feeds, can have a number of benefits for children such as a reduction in GI symptoms or improved overall physical and developmental health.
Educational video demonstrating how to thicken ThickenUp® Clear
Video demonstrating the swallowing process if suffering from dysphagia.
Human milk contains bioactive components that confer protection on the newborn. These include complex carbohydrates called Human Milk Oligosaccharides (HMO). Research is revealing the full extent of the beneficial properties of HMOs. (date 07/10/2019)
Lactose intolerance is one of the more common forms of food intolerance and is often confused with cows' milk allergy. This video explains the differences in both symptoms, diagnosis and treatment. It also explains the different types of lactose intolerance. (date 07/09/2018)
Gerard Minor, is a physician assistant specialising in paediatric gastroenterology and nutrition in Florida. He has carried out a study using Peptamen Jr that was presented at the NASPGHAN conference, Feb 2016, and published in the journal of Global Paediatric Health. Gerard spoke at our ND study day in May 2016 and we recorded his presentation.
Barbara Davidson, Specialist Dietitian from the Freeman Hospital discusses the nutritional challenges of managing acute patients with pancreatitis.
In this brochure, we have collected some of the new and relevant references highlighting the importance of improving the nutritional status among patients, or geriatric individuals, with or at risk of disease-related malnutrition. This brochure includes guidelines for protein and energy requirements, as well as study summaries on the importance of protein quality to regain and build muscle mass. In particular, studies on leucine are included, since this is the most potent amino acid to stimulate muscle protein synthesis. Leucine has been proposed to have a beneficial effect on muscle mass, muscle strength and physical function.
This physical exercise programme provides you with exercises for pre-frail and frail elderly people. You will find a series of exercises adapted to the elderly person's functional capacity (severe limitation, mild and moderate limitation according to the SPPB and Gait Speed), and include exercises for: Strength and power of both arms and legs Balance and walking Flexibility Resistance through cardio exercises All exercises describe the procedure, the initial instructions, frequency and progression for proper monitoring of the patients' prescribed exercises.
This toolkit has been specially designed to ease the work of healthcare professionals during functional and nutritional assessment of their patients with mobility impairment and (risk of) malnutrition. It contains fully validated and internationally recognized screening and diagnosis tools most often used in clinical practice. The aim is to support healthcare professionals with tools to early detect frailty, sarcopenia and malnutrition to ensure timely intervention.
Mobility impairment is characterized by loss of muscle mass, bone mass and function, and may be caused by age-related diseases (e.g. sarcopenia or frailty), acute accidental events (e.g. falls and fractures) and mobility-induced chronic diseases (e.g. osteoarthritis). Nutritional management of malnutrition and mobility impairment typically focus on dietary guidance and may include treatment with oral nutritional supplements (ONS) to provide a high calorie and protein-rich diet of good protein quality. This study summary gives an overview of some key clinical studies on the composition of oral nutrition supplement for the nutritional management of malnutrition and impaired mobility.
Due to reduced levels of physical activity in children with cerebral palsy or other neurodisabilities, there is a risk of tube-fed individuals becoming overweight or obese if their feed contains an excess of calories. Nestlé Health Science provide a nutritionally complete, lower energy formula, Peptamen® Junior 0.6, that can be used to overcome this problem. Peptamen® Junior 0.6 is a well tolerated, low-energy, peptide-based feed with fibre that has been shown to reduce gastrointestinal symptoms in children with neurological impairment. Food for special medical purposes. Enteral tube feed for the dietary management of patients with or at risk of malnutrition. Must be used under medical supervision.